Hot Products
YSX500D 50kW DR system set up and put into service in Cambodia.
YSENMED YSX500D 50kW digital x-ray system has been successfully set up and put into service in a hospital in Cambodia.
YSX056-PE serving as a vehicle-mounted x-ray in the Philippines
YSX056-PE 5.6kW portable x-ray unit has been adapted to fit on a truck, to provide mobile x-ray examination service for remote communities in the Philippines.
X Ray Machine To Zimbabwe
x ray machine, 50KW x ray machine
Microscope To Malawi
Achromatic objectives: 4X、10X、40X(S), 100X(S、Oil) Wide field eyepiece: WF10X(WF16X for option) Eyepiece head: Sliding binocular head inclined at 45° Stage: Double layer mechanical stage size 140X140mm, moving range 75X45mm Focusing: Coaxial coarse and
From Lab to Life: How Automated Blood Component Separators Enhance Patient Care
Views : 1151
Update time : 2024-11-17 14:43:00
In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, technology plays a pivotal role in improving patient outcomes. One such innovation that has made significant strides is the automated blood component separator. If you're wondering how this device impacts patient care, you're in for an enlightening journey. Let's dive into the world of blood component separation and discover how it transforms lives.
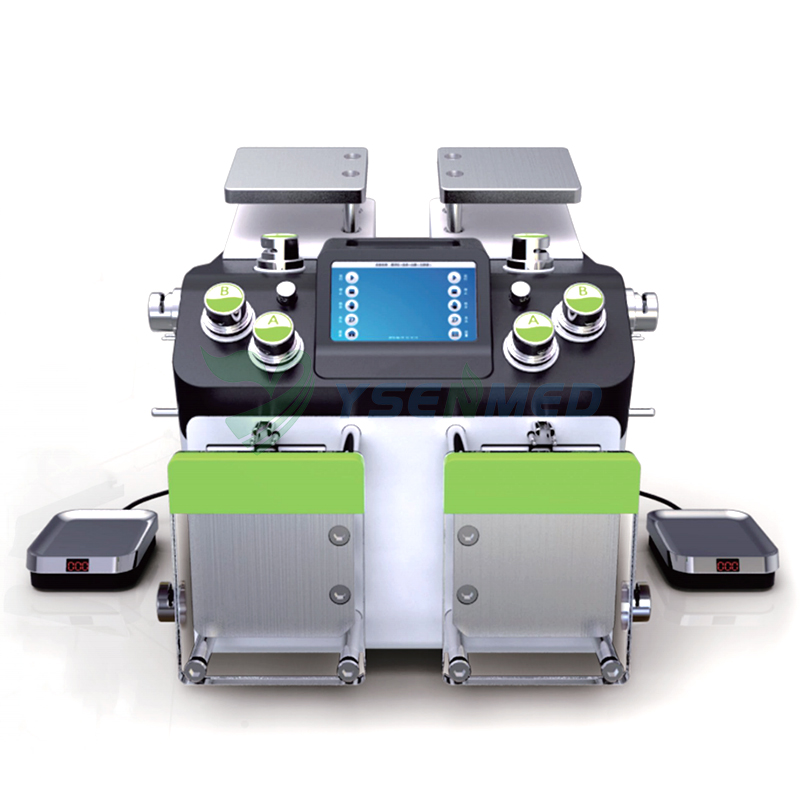

What Are Blood Component Separators?
Blood component separators are specialized machines that separate whole blood into its individual components—red blood cells, plasma, platelets, and white blood cells. This separation is crucial because different patients have different needs; some may require red blood cells for anemia, while others might need platelets for clotting issues.
The Science Behind Blood Separation
Understanding Blood Composition
Before we get into the nitty-gritty of how these machines work, let's take a moment to appreciate what blood is made of. Blood consists of:
- Red Blood Cells (RBCs): Carry oxygen.
- Plasma: The liquid part that transports nutrients, hormones, and waste.
- Platelets: Essential for clotting.
- White Blood Cells (WBCs): Fight infections.
Each component plays a unique role in maintaining health, and separating them allows for targeted treatments.
How Do Automated Separators Work?
Automated blood component separators use a process called centrifugation. Imagine spinning a salad spinner; the centrifugal force pushes heavier items (like the RBCs) to the bottom, while lighter items (like plasma) remain on top. This technology is finely tuned to ensure maximum efficiency and minimal damage to blood cells.
Why Automation Matters
Speed and Efficiency
One of the biggest advantages of automated systems is speed. Traditional methods can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. Automated separators can process multiple units of blood in a fraction of the time, allowing healthcare providers to respond quickly to patient needs.
Consistency and Precision
Automation reduces the risk of human error. With precise algorithms and settings, these machines ensure that blood components are separated uniformly, which is crucial for effective treatment.
Enhancing Patient Care: The Direct Benefits
Targeted Treatments
With separated blood components, healthcare providers can administer targeted treatments. For instance, a single donation can provide red blood cells for one patient, platelets for another, and plasma for yet another. This tailored approach maximizes resources and enhances patient care.
Reduced Risk of Transfusion Reactions
Transfusion reactions can be a serious concern. By using specific components tailored to individual patient needs, the likelihood of adverse reactions decreases significantly. This means safer transfusions and better outcomes.
Improved Inventory Management
Automated systems help hospitals manage their blood inventory more effectively. They can track how much of each component is available, ensuring that critical supplies are always on hand. This real-time management is vital in emergency situations.
Real-World Applications
Emergency Rooms and Trauma Centers
In high-pressure environments like emergency rooms, every second counts. Automated blood component separators enable rapid access to the necessary blood components, which can be lifesaving for trauma patients. Imagine a car accident where every moment matters; having immediate access to the right blood components can make all the difference.
Cancer Treatment
Patients undergoing chemotherapy often require platelets due to treatment-induced thrombocytopenia (low platelet count). Automated separators can quickly provide the necessary platelets, ensuring that patients can continue their treatment without delay.
Surgical Procedures
During surgeries, especially major ones, the need for blood components can increase dramatically. Automated systems ensure that hospitals can quickly supply the needed components, enhancing surgical outcomes and patient recovery times.
The Future of Blood Component Separation
Advancements in Technology
As technology continues to evolve, so will blood component separators. Innovations like artificial intelligence and machine learning could further enhance the efficiency and accuracy of these machines. Imagine a future where these devices can predict the exact components needed for specific patients based on real-time data!
Integration with Telemedicine
With the rise of telemedicine, integrating automated blood component separators with remote patient monitoring could revolutionize patient care. Physicians could monitor blood needs remotely and ensure timely delivery of components, even in rural areas.
Challenges and Considerations
Initial Costs
While the benefits are clear, the initial investment for automated systems can be high. Hospitals must weigh the costs against the potential long-term savings and improved patient outcomes.
Training and Adaptation
Staff must be trained to operate these advanced machines effectively. Transitioning from traditional methods to automated systems requires time and effort but pays off in the long run.
Conclusion: A Leap Towards Better Patient Care
In summary, automated blood component separators are more than just machines; they are game changers in the healthcare industry. By enhancing the precision, speed, and safety of blood component separation, they significantly improve patient care. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even greater innovations that will further enhance the way we approach blood transfusions and treatments. So, the next time you hear about blood donation, remember the incredible journey it takes from lab to life, and how these automated systems play a crucial role in saving lives.
FAQ
What is an automated blood component separator?
An automated blood component separator is a medical device that separates whole blood into its individual components, such as red blood cells, plasma, platelets, and white blood cells. This technology uses centrifugation to efficiently and precisely separate these components, allowing for targeted treatments based on patient needs.
How does the separation process work?
The separation process involves centrifugation, where blood is spun at high speeds. The centrifugal force causes the heavier components, like red blood cells, to settle at the bottom, while lighter components, such as plasma, rise to the top. This allows healthcare providers to collect specific components for transfusion or treatment.
Are there any risks associated with blood component separation?
While the process itself is generally safe, there can be risks associated with blood transfusions, such as allergic reactions or infections. However, using automated separators can minimize these risks by ensuring that patients receive the specific components they need, which reduces the likelihood of adverse reactions.

What Are Blood Component Separators?
Blood component separators are specialized machines that separate whole blood into its individual components—red blood cells, plasma, platelets, and white blood cells. This separation is crucial because different patients have different needs; some may require red blood cells for anemia, while others might need platelets for clotting issues.
The Science Behind Blood Separation
Understanding Blood Composition
Before we get into the nitty-gritty of how these machines work, let's take a moment to appreciate what blood is made of. Blood consists of:
- Red Blood Cells (RBCs): Carry oxygen.
- Plasma: The liquid part that transports nutrients, hormones, and waste.
- Platelets: Essential for clotting.
- White Blood Cells (WBCs): Fight infections.
Each component plays a unique role in maintaining health, and separating them allows for targeted treatments.
How Do Automated Separators Work?
Automated blood component separators use a process called centrifugation. Imagine spinning a salad spinner; the centrifugal force pushes heavier items (like the RBCs) to the bottom, while lighter items (like plasma) remain on top. This technology is finely tuned to ensure maximum efficiency and minimal damage to blood cells.
Why Automation Matters
Speed and Efficiency
One of the biggest advantages of automated systems is speed. Traditional methods can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. Automated separators can process multiple units of blood in a fraction of the time, allowing healthcare providers to respond quickly to patient needs.
Consistency and Precision
Automation reduces the risk of human error. With precise algorithms and settings, these machines ensure that blood components are separated uniformly, which is crucial for effective treatment.
Enhancing Patient Care: The Direct Benefits
Targeted Treatments
With separated blood components, healthcare providers can administer targeted treatments. For instance, a single donation can provide red blood cells for one patient, platelets for another, and plasma for yet another. This tailored approach maximizes resources and enhances patient care.
Reduced Risk of Transfusion Reactions
Transfusion reactions can be a serious concern. By using specific components tailored to individual patient needs, the likelihood of adverse reactions decreases significantly. This means safer transfusions and better outcomes.
Improved Inventory Management
Automated systems help hospitals manage their blood inventory more effectively. They can track how much of each component is available, ensuring that critical supplies are always on hand. This real-time management is vital in emergency situations.
Real-World Applications
Emergency Rooms and Trauma Centers
In high-pressure environments like emergency rooms, every second counts. Automated blood component separators enable rapid access to the necessary blood components, which can be lifesaving for trauma patients. Imagine a car accident where every moment matters; having immediate access to the right blood components can make all the difference.
Cancer Treatment
Patients undergoing chemotherapy often require platelets due to treatment-induced thrombocytopenia (low platelet count). Automated separators can quickly provide the necessary platelets, ensuring that patients can continue their treatment without delay.
Surgical Procedures
During surgeries, especially major ones, the need for blood components can increase dramatically. Automated systems ensure that hospitals can quickly supply the needed components, enhancing surgical outcomes and patient recovery times.
The Future of Blood Component Separation
Advancements in Technology
As technology continues to evolve, so will blood component separators. Innovations like artificial intelligence and machine learning could further enhance the efficiency and accuracy of these machines. Imagine a future where these devices can predict the exact components needed for specific patients based on real-time data!
Integration with Telemedicine
With the rise of telemedicine, integrating automated blood component separators with remote patient monitoring could revolutionize patient care. Physicians could monitor blood needs remotely and ensure timely delivery of components, even in rural areas.
Challenges and Considerations
Initial Costs
While the benefits are clear, the initial investment for automated systems can be high. Hospitals must weigh the costs against the potential long-term savings and improved patient outcomes.
Training and Adaptation
Staff must be trained to operate these advanced machines effectively. Transitioning from traditional methods to automated systems requires time and effort but pays off in the long run.
Conclusion: A Leap Towards Better Patient Care
In summary, automated blood component separators are more than just machines; they are game changers in the healthcare industry. By enhancing the precision, speed, and safety of blood component separation, they significantly improve patient care. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even greater innovations that will further enhance the way we approach blood transfusions and treatments. So, the next time you hear about blood donation, remember the incredible journey it takes from lab to life, and how these automated systems play a crucial role in saving lives.
FAQ
What is an automated blood component separator?
An automated blood component separator is a medical device that separates whole blood into its individual components, such as red blood cells, plasma, platelets, and white blood cells. This technology uses centrifugation to efficiently and precisely separate these components, allowing for targeted treatments based on patient needs.
How does the separation process work?
The separation process involves centrifugation, where blood is spun at high speeds. The centrifugal force causes the heavier components, like red blood cells, to settle at the bottom, while lighter components, such as plasma, rise to the top. This allows healthcare providers to collect specific components for transfusion or treatment.
Are there any risks associated with blood component separation?
While the process itself is generally safe, there can be risks associated with blood transfusions, such as allergic reactions or infections. However, using automated separators can minimize these risks by ensuring that patients receive the specific components they need, which reduces the likelihood of adverse reactions.
Related News
Read More >>
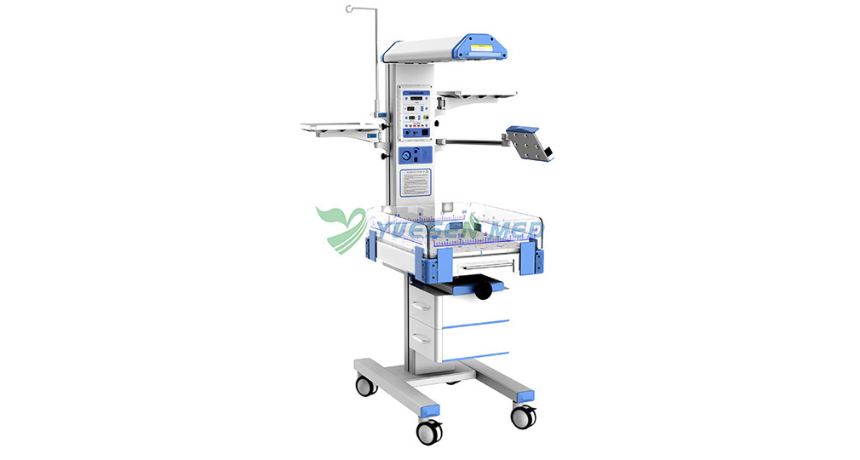 What is the Difference Between Radiant Warmer and Phototherapy?
What is the Difference Between Radiant Warmer and Phototherapy?
Apr .19.2025
Radiant warmers and phototherapy are crucial in neonatal care, but they serve different purposes. Let's dive into the nitty-gritty of these two techniques and explore how they differ, and when each is appropriate.
 YSX056-PE portable digital x-ray unit set up in the Philippines
YSX056-PE portable digital x-ray unit set up in the Philippines
Apr .19.2025
YSX056-PE portable digital x-ray unit has been set up in a hospital in the Philippines and the good quality images please the doctors.
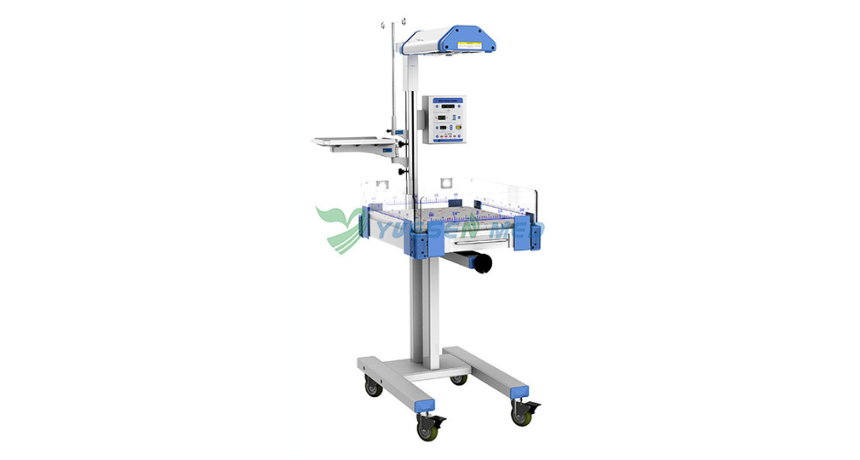 Is an Infant Radiant Warmer Good for Babies' Health?
Is an Infant Radiant Warmer Good for Babies' Health?
Apr .13.2025
What exactly is the infant radiant warmer, and how does it contribute to a baby's health? Let's dive into this topic and explore the ins and outs of infant radiant warmers.
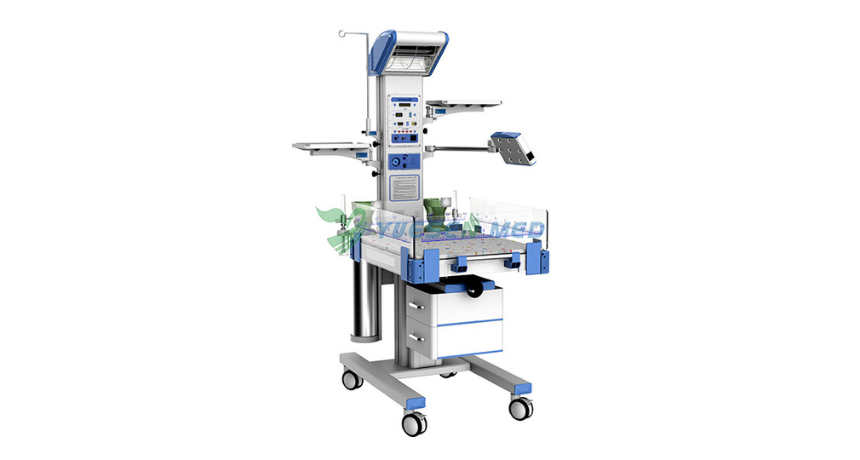 What is an Infant Radiant Warmer?
What is an Infant Radiant Warmer?
Apr .12.2025
One of the unsung heroes in neonatal care is the infant radiant warmer. But what exactly is it? Let's dive into the world of infant care and explore the ins and outs of this vital device.



